Address
Mataram, Nusa Tenggara Barat, Indonesia
Work Hours
Monday to Thursday : 9AM - 5PM
Fryday: 9AM - 4PM
Address
Mataram, Nusa Tenggara Barat, Indonesia
Work Hours
Monday to Thursday : 9AM - 5PM
Fryday: 9AM - 4PM

Vocational High School (SMK) graduates are prepared to become skilled workers who are ready to enter the Business and Industrial World (DUDI). However, there is a paradox in the national and regional regions, including in West Nusa Tenggara (NTB). Data from the Central Statistics Agency (BPS) of NTB consistently shows that the Open Unemployment Rate (TPT) of vocational school graduates often contributes the highest number.
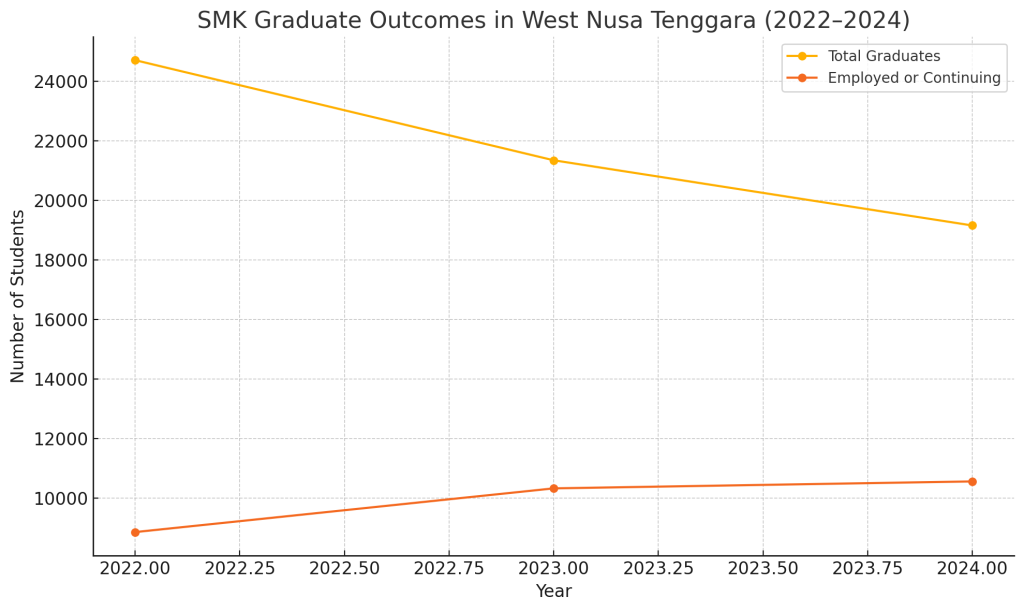
Figure 4. The gap between the number of vocational school graduates and the number of vocational school graduates who work or continue their studies
This problem indicates that there is a gap between the competencies taught in schools and the real needs of the students. More specifically, rodents not only require technical skills (hard skills), but also demand soft skills such as work ethic, communication, problem-solving skills, and teamwork that are often not honed.
The current internship program (Prakerin) is sometimes rocedulal and has not focused on developing soft skills in a structured manner.
Responding to this challenge, the Sino International Research and Development Foundation, through the pillars of “Workshop” and “Coaching”, initiated the “Vocational School Student Soft Skill Improvement Program” as a strategic intervention to increase the absorption of vocational school graduates in Lombok, NTB.
2. Program Objectives
General Objective: To increase the employability (employability of vocational school graduates in Lombok, NTB, by bridging the soft skills gap needed by the industry.
Special Purpose:
3. Program Needs Analysis & Justification
The need for this program is based on three pillars of analysis:
4. Program Mechanism and Partner Roles
This program is a tripartite collaboration between Foundations, Vocational Schools, and Industry (DUDI), which is implemented in three phases:
Table 5. Program Mechanism and Partner Roles
| Phase | Main Activities | Foundation Role (Sino R&D) | Partner Vocational School Role (SMK) | Partner Industry Role (DUDI) |
| Phase 1: Preparation (Pre-Internship) | Soft-Skill Bootcamp & Industry Mapping | Deliver “Professional Mindset” workshops; select partner industries. | Select students; integrate bootcamp into curriculum. | Provide internship criteria and vacancies. |
| Phase 2: Implementation (Internship) | Structured Internship & Coaching | Provide modules & soft-skill logbook; regular coaching and monitoring. | Assign supervising teachers. | Assign mentors; provide real tasks and performance feedback. |
| Phase 3: Evaluation (Post-Internship) | Debriefing & Performance Assessment | Conduct evaluation sessions; issue Soft-Skill Certificates. | Curriculum review based on feedback. | Final assessment and potential recruitment. |
5. Long-Term Impact Projections
Interventions on soft skills at the vocational school level will have a significant chain impact on the employment ecosystem in NTB.
Table 6. Structured Internship Program Impact Projection Table
| Time Frame | Student Impact Projection | Ecosystem Impact Projection |
| Short-Term (Year 1) | Students gain professional mindset and real work portfolios; higher interview confidence. | 2 partner SMKs and 5 industries piloted; industries receive better intern support. |
| Medium-Term (Years 2–3) | 15–20% increase in employability rate of partner school graduates; shorter waiting period for employment. | Structured internship model replicated wider; Foundation recognized as SMK talent hub. |
| Long-Term (Years 4–5) | NTB vocational graduates renowned for work ethic and soft skills comparable to developed regions. | Gradual decrease in vocational graduate unemployment; systemic curriculum improvement via industry feedback. |